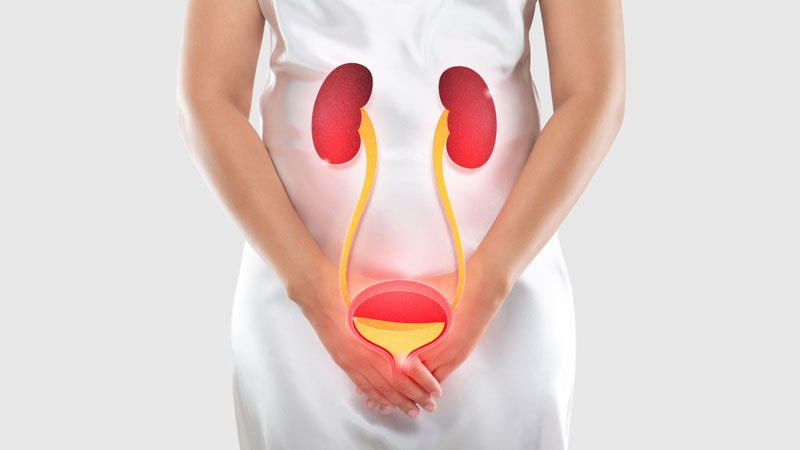
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra.
A UTI is caused by bacteria entering the urinary tract, leading to infection. Common symptoms include a strong, persistent urge to urinate, a burning sensation when urinating, cloudy urine, strong-smelling urine, pelvic pain in women, and, occasionally, blood in the urine.
UTI treatment generally involves:
Nebulizers are not used for UTIs. Alternatives and preventive measures include: