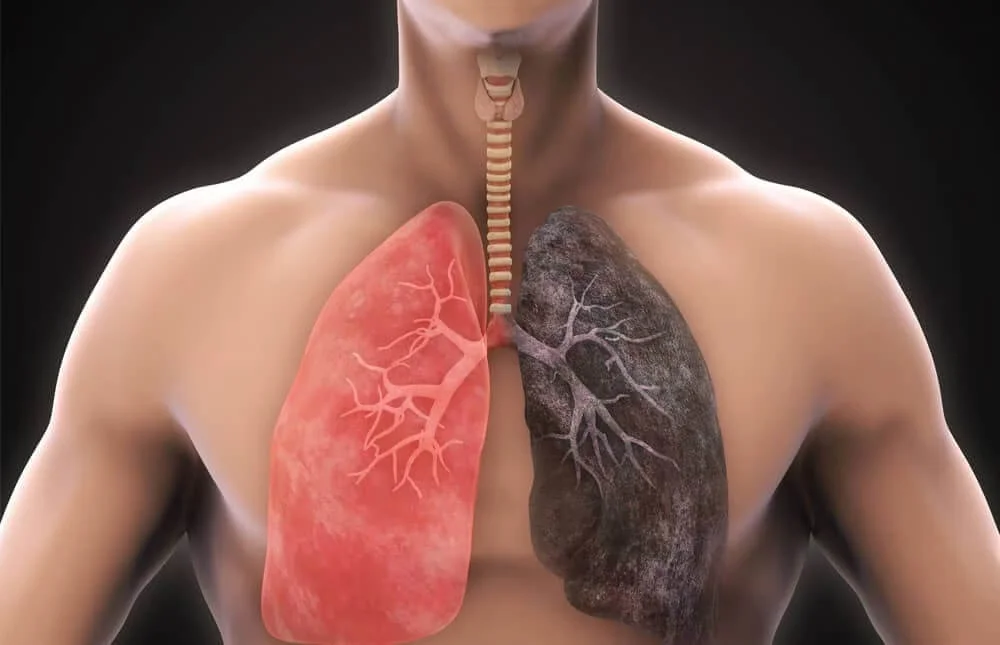
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease characterized by airflow limitation and difficulty breathing. It encompasses conditions such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema, typically caused by long-term exposure to irritants like cigarette smoke or environmental pollutants. Understanding COPD, its symptoms, and management strategies is essential for improving quality of life and slowing […]
COPD is a chronic lung condition characterized by persistent airflow limitation, making it difficult to breathe. It is primarily caused by exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, or occupational dust and chemicals. COPD includes two main conditions: chronic bronchitis, involving inflammation and narrowing of the airways, and emphysema, involving damage to the air sacs in the lungs.
Diagnosing and managing COPD typically involves several steps:
Understanding COPD and implementing comprehensive management strategies can help individuals with COPD lead fulfilling lives and maintain optimal respiratory health. Regular medical follow-up, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications are essential components of COPD management.