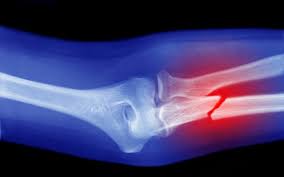
Broken bones, also known as fractures, occur when a force exerted against a bone is stronger than the bone can bear. Fractures can happen due to falls, accidents, sports injuries, or other traumatic events. They require medical attention to ensure proper healing and to avoid complications.
A broken bone or fracture is a condition where there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of the bone. Fractures can be classified into several types, including simple (closed), compound (open), comminuted (shattered), and stress fractures. Symptoms typically include pain, swelling, bruising, and inability to move the affected area.
The treatment procedure for broken bones generally involves the following steps:
While nebulizers are not used for bone injuries, alternative treatment options for managing pain and promoting healing include: