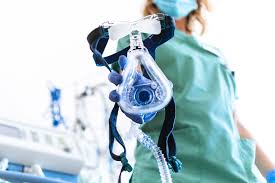
Breathing treatments, also known as nebulizer treatments, are medical interventions used to administer medication directly into the lungs. These treatments are commonly used for individuals with respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other lung diseases. The medication, often in liquid form, is converted into a mist that can be easily […]
Breathing treatment refers to the use of a nebulizer to deliver medication directly into the lungs. A nebulizer is a medical device that turns liquid medication into a fine mist, which can be inhaled deeply into the airways. This method ensures that the medication reaches the respiratory system quickly and efficiently, providing relief from symptoms and improving breathing.
During a breathing treatment, the following steps typically occur: